
The SpatioTemporal Omics Consortium (STOC) is a collaborative analysis initiative that goals to speed up our understanding of mobile complexity and interactions at tissue scale in growth, physiology, and illness by means of large-scale spatially resolved multiomics analyses.
Worldwide scientific consortium, the SpatioTemporal Omics Consortium (STOC), produces the primary spatiotemporal maps of mobile dynamics in mice, Drosophila, zebrafish, and Arabidopsis, utilizing BGI-Analysis’s world-leading Stereo-seq expertise.
A world staff of scientists led by China’s BGI-Analysis revealed state-of-the-art panoramic spatial atlases of life, inspecting the mobile dynamics of organisms at totally different developmental phases and offering probably vital new data for illness remedy, growth, and growing old, and an improved understanding of organic evolution.
In a collection of research revealed in Cell Press journals, STOC members used the spatially resolved transcriptomics expertise Stereo-seq, developed by BGI-Analysis, to supply spatiotemporal mobile maps of mice, small fruit flies (Drosophila), zebrafish, and the Arabidopsis plant. The papers show how Stereo-seq has achieved a serious breakthrough in spatial decision and panoramic area of view, enabling evaluation of the distribution and placement of molecules and cells in situ, and over time.
The paper, Spatiotemporal transcriptomic atlas of mouse organogenesis utilizing DNA nanoball-patterned arrays, is revealed in Cell. The opposite three research on Drosophila, zebrafish and Arabidopsis are revealed in Developmental Cell. Figuring out the traits of particular cells inside a tissue has vital functions for understanding which cells are causes or indicators of illness, probably resulting in future good points in human illness analysis.
“Previously, it took 1000's and even tens of 1000's of experiments to finish a spatiotemporal map. Now, with Stereo-seq developed by our scientists, it may be achieved rapidly and comprehensively with one. This can be a milestone breakthrough in life sciences technogy development,” stated Dr. Chen Ao, who led the event of the Stereo-seq expertise at BGI-Analysis and is the primary writer of the mouse spatiotemporal atlas paper.
Greater than 80 scientists from 16 international locations, together with scientists from Harvard College, Massachusetts Institute of Know-how, Oxford College, College of Cambridge, the College of Western Australia, the Karolinska Institutet, the Genome Institute of Singapore, and BGI, have to date collaborated as a part of STOC, an open scientific collaboration consortium centered on utilizing spatially resolved, mobile decision omics applied sciences to map and perceive life.
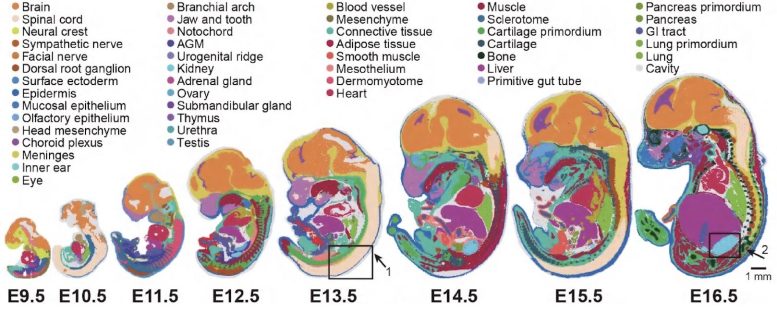
Graphic of early embryonic growth of mice from 9.5 to 16.5 days utilizing Stereo-seq expertise. Credit score: BGI Group
Spatial transcriptomics expertise is an rising expertise that resolves earlier points figuring out traits of single cells inside a organic tissue. It builds on the achievements of single-cell sequencing, elevating it to the following stage by enabling scientists to trace a cell’s exact location and the way it interacts with its neighbors.
To attain this, BGI’s personal sequencing patented DNA nanoball expertise, which amplifies small fragments of DNA into bigger samples, was mixed with its in situRNA seize expertise to create Stereo-seq (SpaTial Enhanced REsolution Omics-sequencing), able to attaining a subcellular decision of 500 nanometers (equal to 0.0000005 meter) mixed with a panoramic centimeter-level area of view.
“The event of single cell analytical strategy over the previous twenty years has actually made a outstanding distinction in our skill to know how cells differ from one another. Extra just lately, it began to be doable to mix that evaluation with the place cells are in a tissue or organoid tissue part,” stated Patrick Maxwell, Regius Professor of Physic and Head of the Faculty of Medical Medication at Cambridge, and co-author of the mouse spatiotemporal atlas paper. “For my part, this new paper takes this to a brand new stage by combining a considerable dimension area of view, making doable to research a tissue on a scale of a creating mouse embryo, along with a really excessive decision with a really deep transcriptomic learn depth.”
“This permits us and the customers of this information, which will likely be freely out there, to essentially begin to perceive some very fascinating questions on how mammalian growth works, and the way tissues are organized. That may give us insights into developmental processes, regular tissue operate, and likewise illnesses,” he added.
If we evaluate the examine of cells to the examine of the ecosystem, earlier applied sciences allowed scientists to know which animals or crops are on earth. With Stereo-seq, scientists can perceive which nation, which space, which habitat, and which neighborhood all animals or crops belong to. On the identical time, scientists may also perceive what every animal is doing, their previous, household historical past, interplay with different herds, and the way they might proliferate and develop.
The scientists used Stereo-seq to look at the early embryonic growth of mice, particularly from 9.5 to 16.5 days throughout which embryonic growth is going on at a quick price. Stereo-seq generated the Mouse Organogenesis Spatiotemporal Transcriptomic Atlas (MOSTA), which maps the kinetics and directionality of transcriptional variation throughout mouse organogenesis with single-cell decision and excessive sensitivity.
“Stereo-seq is a transformational breakthrough in spatial transcriptomics expertise and is essentially the most highly effective expertise on this area of life sciences as we speak,” stated Dr. Liu Longqi of BGI-Analysis, one of many corresponding authors of the papers. “We now have a expertise to map a panoramic atlas of each cell in an organism, based on their particular person biomolecular profiles, in area and over time. We've demonstrated its robustness, and efficiently mapped each animal and plant molecular physiology at a scale and determination by no means earlier than doable.”
For the primary time the scientists have been in a position to produce a collection of high-definition maps displaying the exact location of the roughly 300,000 cells from the day 16.5 embryo. BGI-Analysis used this data to supply a panoramic atlas of the mouse and achieve perception into the molecular foundation of cell variation and differentiation in creating tissues of the mind, together with the dorsal midbrain.
“The profitable utility of our Stereo-seq expertise for growth has vital implications for the way forward for genomic analysis on human illnesses,” stated co-corresponding writer Dr. Xu Xun, director of BGI-Analysis. “Demonstrating that this expertise can pinpoint sure cells which point out future illness will likely be essential for diagnostics and therapeutics for various situations.”
For instance, Robinow syndrome is a typical start defect. A gene associated to this has been discovered clinically, however how this gene causes defects together with cleft lip and palate, and limb shortness, is unknown. The researchers mapped the cleft lip and palate-related gene within the technique of mouse embryonic growth, and located that the gene was current within the lips and toes of the mouse, and confirmed excessive expression. This demonstrated that the gene is essential within the growth of lips and toes in mice. If this gene is mutated, the event of lips and toes will likely be irregular. This data will probably assist researchers learning Robinow syndrome start defects in people.
The BGI-led staff carried out related embryonic analysis with the zebrafish which has a gestation interval of solely 24 hours, and likewise produced a 3D mannequin of the mobile map of the small fruit fly Drosophila. The spatiotemporal transcriptomic atlas of embryonic growth in Drosophila, zebrafish, and mouse has opened new doorways for the examine of embryonic patterning and associated molecular mechanisms throughout embryonic growth, offering vital information references for additional work in addition to for a benchmark for unraveling embryonic evolution.
By making use of Stereo-seq analysis on the leaf cells of the Arabidopsis plant, the researchers have been in a position to overcome the long-term problem for researchers to conduct spatially resolved single-cell omics research on leaves and different plant tissues. BGI-Analysis was in a position to show that Stereo-seq expertise will be utilized in plant scientific analysis and crop breeding analysis. Some key functions embrace understanding key genes concerned in seed growth, mechanisms behind drought resistance, mechanisms behind warmth resistance, and mechanisms behind salt tolerance, for staple crops from rice to wheat to maize. This might contribute to the cultivation of high-quality, stress-resistant crop strains vital for a lot of international sustainability initiatives.
The research obtained all needed moral clearance earlier than they have been performed.
References:
“Spatiotemporal transcriptomic atlas of mouse organogenesis utilizing DNA nanoball-patterned arrays” by Ao Chen, Sha Liao, Mengnan Cheng, Kailong Ma, Liang Wu, Yiwei Lai, Xiaojie Qiu, Jin Yang, Jiangshan Xu, Shijie Hao, Xin Wang, Huifang Lu, Xi Chen, Xing Liu, Xin Huang, Zhao Li, Yan Hong, Yujia Jiang, Jian Peng, Shuai Liu, Mengzhe Shen, Chuanyu Liu, Quanshui Li, Yue Yuan, Xiaoyu Wei, Huiwen Zheng, Weimin Feng, Zhifeng Wang, Yang Liu, Zhaohui Wang, Yunzhi Yang, Haitao Xiang, Lei Han, Baoming Qin, Pengcheng Guo, Guangyao Lai, Pura Muñoz-Cánoves, Patrick H. Maxwell, Jean Paul Thiery, Qing-Feng Wu, Fuxiang Zhao, Bichao Chen, Mei Li, Xi Dai, Shuai Wang, Haoyan Kuang, Junhou Hui, Liqun Wang, Ji-Feng Fei, Ou Wang, Xiaofeng Wei, Haorong Lu, Bo Wang, Shiping Liu, Ying Gu, Ming Ni, Wenwei Zhang, Feng Mu, Ye Yin, Huanming Yang, Michael Lisby, Richard J. Cornall, Jan Mulder, Mathias Uhlén, Miguel A. Esteban, Yuxiang Li, Longqi Liu, Xun Xu and Jian Wang, 4 Could 2022, Cell.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.003
“Spatiotemporal mapping of gene expression landscapes and developmental trajectories throughout zebrafish embryogenesis” by Chang Liu, Rui Li, Younger Li, Xiumei Lin, Kaichen Zhao, Qun Liu, Shuowen Wang, Xueqian Yang, Xuyang Shi, Yuting Ma, Chenyu Pei, Hui Wang, Wendai Bao, Junhou Hui, Tao Yang, Zhicheng Xu, Tingting Lai, Michael Arman Berberoglu, Sunil Kumar Sahu, Miguel A. Esteban, Kailong Ma, Guangyi Fan, Yuxiang Li, Shiping Liu, Ao Chen, Xun Xu, Zhiqiang Dong and Longqi Liu, 4 Could 2022, Developmental Cell.
DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.04.009
“The one-cell stereo-seq reveals region-specific cell subtypes and transcriptome profiling in Arabidopsis leaves” by Keke Xia, Hai-Xi Solar, Jie Li, Jiming Li, Yu Zhao, Lichuan Chen, Chao Qin, Ruiying Chen, Zhiyong Chen, Guangyu Liu, Ruilian Yin, Bangbang Mu, Xiaojuan Wang, Mengyuan Xu, Xinyue Li, Peisi Yuan, Yixin Qiao, Shijie Hao, Jing Wang, Qing Xie, Jiangshan Xu, Shiping Liu, Yuxiang Li, Ao Chen, Longqi Liu, Ye Yin, Huanming Yang, Jian Wang, Ying Gu and Xun Xu, 4 Could 2022, Developmental Cell.
DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.04.011
“Excessive-resolution 3D spatiotemporal transcriptomic maps of creating Drosophila embryos and larvae” by Mingyue Wang, Qinan Hu, Tianhang Lv, Yuhang Wang, Qing Lan, Rong Xiang, Zhencheng Tu, Yanrong Wei, Kai Han, Chang Shi, Junfu Guo, Chao Liu, Tao Yang, Wensi Du, Yanru An, Mengnan Cheng, Jiangshan Xu, Haorong Lu, Wangsheng Li, Shaofang Zhang, Ao Chen, Wei Chen, Yuxiang Li, Xiaoshan Wang, Xun Xu, Yuhui Hu and Longqi Liu, 4 Could 2022, Developmental Cell.
DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.04.006
0 Response to "Cellular Dynamics: First Panoramic Spatial Atlases of Life"
Posting Komentar